Guest spending boosts US economy by a record $90 billion in 2024
Key Takeaways
- According to newly released estimates, travel on Airbnb generated more than $90B in economic activity across the United States in 2024
- The influx of visitor spending helped support more than one million estimated jobs nationwide last year – a new record – helping to generate over $52B in labor income.
- While many communities continue to benefit from tourism on Airbnb, a new study finds that strict short-term rental rules led to major cities potentially losing as much as $2.4B in economic activity annually combined – including $1.6B in forgone guest spending at local restaurants, shops, and entertainment venues.

Key Takeaways
- According to newly released estimates, travel on Airbnb generated more than $90B in economic activity across the United States in 2024
- The influx of visitor spending helped support more than one million estimated jobs nationwide last year – a new record – helping to generate over $52B in labor income.
- While many communities continue to benefit from tourism on Airbnb, a new study finds that strict short-term rental rules led to major cities potentially losing as much as $2.4B in economic activity annually combined – including $1.6B in forgone guest spending at local restaurants, shops, and entertainment venues.
In 2024, Airbnb marked a major milestone with our 2 billionth guest arrival when Wisconsin retirees Tim and Theresa stayed in a spectacular Guest Favorite Airbnb in Sandy, Utah, with their family. All across the country, travelers like Tim and Theresa are booking Airbnbs to reconnect with loved ones and experience new destinations. In doing so, they’re also supporting local economies – from small towns to big cities – and driving meaningful economic impact into every corner of the country.
According to newly released estimates, travel on Airbnb generated more than $90 billion in economic activity across the United States in 20241 – a record figure reflecting the total contribution driven by guests, hosts, and the businesses guests support.
For the first time ever, travel on Airbnb helped support over one million U.S. jobs
According to the findings, in 2024, the typical guest in the US spent more than $775 per trip on other goods and services like restaurants, entertainment, shopping, and other local businesses2. That influx of visitor spending helped support more than one million estimated jobs nationwide last year, helping to generate over $52 billion in labor income.
And because many Airbnb listings are located outside traditional hotel zones, these benefits are widely dispersed. In fact, nearly 50 percent of guest spending occurred in the neighborhood of their Airbnb3 – helping generate economic activity in places that might not otherwise attract tourism dollars.
The benefits also support local governments. Travel on Airbnb generated over $25 billion in total tax revenue across the U.S.4, including $2.4 billion in tourism-related taxes collected and remitted by Airbnb on behalf of hosts at a time when governments are facing budget shortfalls.
Over-regulation leads to major cities putting at risk $2.4B in economic activity
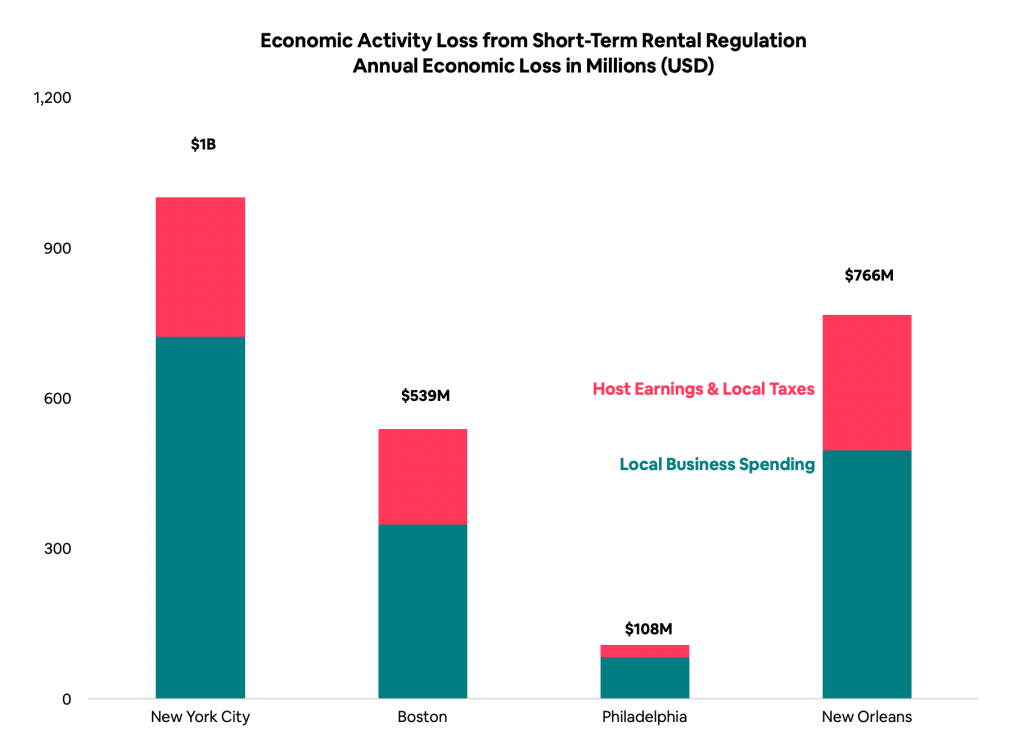
While many communities continue to benefit from tourism on Airbnb, a new study by leading economic consulting firm Charles River Associates commissioned by Airbnb finds that over-regulation may cost some major cities billions of dollars.
In New York City, Philadelphia, Boston, and New Orleans, strict short-term rental rules led to these cities potentially losing as much as $2.4 billion in economic activity annually combined – including $1.6 billion in forgone guest spending at local restaurants, shops, and entertainment venues5.
Local businesses that support home sharing – such as cleaners, maintenance providers, and laundry services – are also missing out, having potentially lost an estimated $150 million annually in revenue in these cities.
The report also finds that hotels were the primary beneficiaries of strict short-term rental laws – at the expense of nearly everyone else: renters, visitors, local residents, and local governments. Ultimately, as travel demand remained strong, fewer accommodation options, particularly in New York City pushed hotel prices higher – forcing many guests to spend more on lodging and less in the communities they came to explore – all without a meaningful impact on housing affordability or availability.
According to the report, local governments may have lost nearly $200 million in tax revenue each year, with New York City alone forfeiting $82 million – money that could have been used to build more affordable housing and help alleviate the ongoing housing crisis. These regulations, ostensibly put in place to improve housing affordability and availability, have not netted the intended results. Rent in New York City following Local Law 18, for example, has reached record heights, and vacancy rates remained unchanged.
This forfeited economic opportunity comes at the same time that cities face growing deficits, putting jobs and municipal services at risk.
Airbnb’s economic impact spans all 50 states
The economic contributions of Airbnb travel are felt in every corner of the country – helping to boost local economies, support small businesses, and generate critical revenue for state and local governments. Click here or use the map below to better understand the impact Airbnb hosts and guests have in all 50 states.
Methodological and legal note:
The analysis was carried out using the IMPLAN economic model, which considers three levels of impact:
- Direct: refers to the immediate effects of an economic activity. In the context of tourism, the direct economic impact is the initial expenditure by tourists on goods and services during their trips. This expenditure includes items such as accommodation, meals, transportation, attractions, and souvenirs.
- Indirect: refers to the secondary effects generated by the initial expenditure on related industries that supply goods and services to the primary industry. These industries provide inputs or support services necessary for the operation of the primary industry.
- Induced: refers to the tertiary effects resulting from increased household spending by employees of directly and indirectly affected industries. This includes the expenditure of income generated by employees related to, or resulting from, economic activity.
IMPLAN is a regional economic analysis software program designed to estimate the impact or ripple effects (specifically, indirect linkages) of a given economic activity within a specific geographic area by applying its input-output matrix and social accounting model. Studies, results, and reports based on IMPLAN data or applications are limited by the assumptions of the researchers regarding the subject of the event being modeled. Studies such as this one are in no way endorsed or verified by IMPLAN Group, LLC, unless otherwise indicated by an IMPLAN representative.
The ratings, percentages, and economic data included in this release are based on internal information from the Airbnb platform collected during 2024, as well as on studies prepared or commissioned by Airbnb to analyze the economic impact of digital tourism in the US. This release is for informational purposes only and does not constitute a guarantee or commercial representation regarding the quality, availability, or characteristics of the spaces listed on the platform.
About IMPLAN
As the leading provider of economic impact data and analytical applications, we have spent decades serving the economic data needs of researchers, policymakers, decision-makers, advocates, business leaders, governments, and more.
IMPLAN has been redefining the field of economics for over 40 years. Created by academics to serve the needs of the U.S. Forest Service, it has now transformed to serve as a solutions provider for anyone interested in understanding their economics.